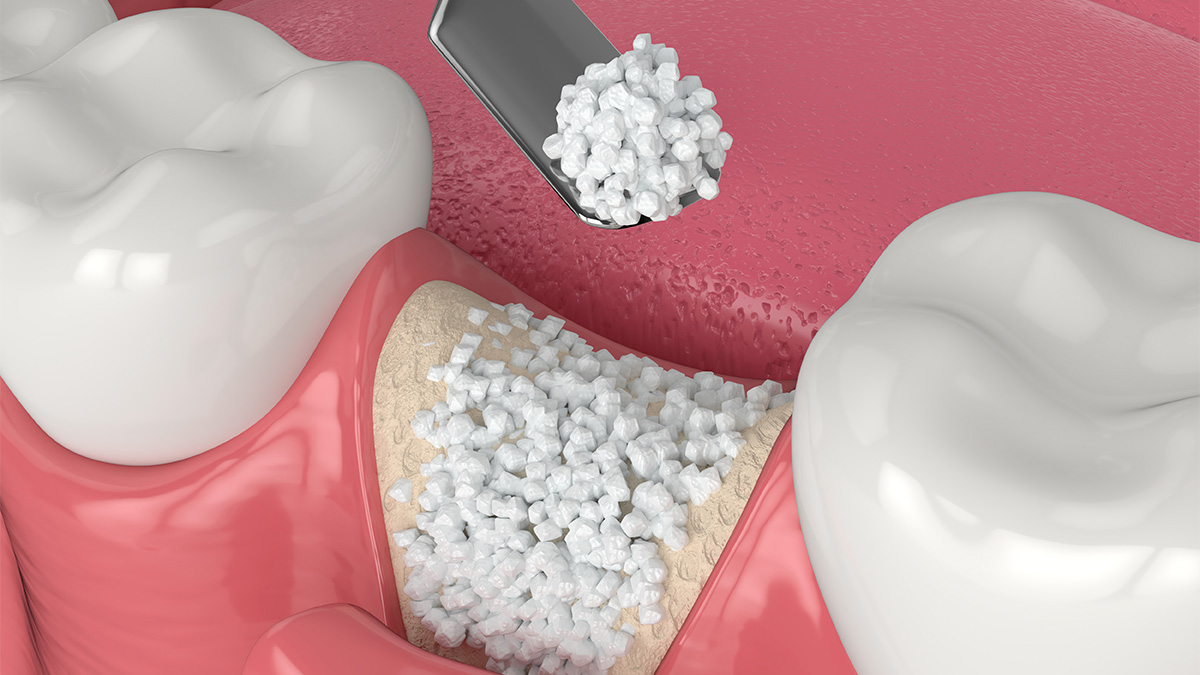
Bone Augmentation
Bone augmentation is a procedure used to increase the quantity or quality of bone in the area of a tooth or jaw. This may be necessary for various reasons, such as preparing for dental implant placement or addressing bone resorption issues. Here are some key aspects of bone augmentation:
Indications:
- Preparation for Implantation: When a patient wants to receive dental implants but lacks sufficient bone in the area where the implants will be placed. Bone is needed to securely anchor the implants.
- Correction of Bone Atrophy: Bone atrophy, or bone loss, can occur due to various reasons, including prolonged tooth loss, periodontal disease, or trauma. Augmentation can be used to repair damaged bone.
- Aesthetic Purposes: Sometimes, augmentation is performed for aesthetic reasons to achieve the desired appearance of the jaw or teeth.
Preparation:
- Diagnosis: The first step is to diagnose the patient’s condition through X-rays and a clinical examination to determine the need for augmentation.
- Planning: Based on the diagnosis, the dentist will create a treatment plan that includes the type of augmentation and the materials that will be used.
Methods: There are several different methods for bone augmentation:
- Autologous Bone: In this method, the patient’s own bone (often from the lower jaw or pelvic bone) is used to increase bone in the needed area.
- Bone Substitute Materials: Artificial materials like synthetic bones, banked bones, or animal bones are used to supplement existing bone.
- Membranes: Sometimes, membranes are used to maintain space and encourage bone regeneration.
- Sinus Lift: This specific technique is used to augment bone in the upper jaw, especially in the sinus area.
Procedure:
- Anesthesia: The patient will be locally anesthetized to ensure a painless procedure.
- Preparation of the Area: The dentist will open the tissue to access the bone and prepare it for augmentation.
- Augmentation: The chosen augmentation method is applied according to the treatment plan.
- Wound Closure: After the augmentation is completed, the wound is closed with stitches.
Recovery: Recovery after bone augmentation can vary depending on the type and extent of the procedure. The dentist will provide the patient with care and hygiene instructions, and may prescribe medications for pain and inflammation relief. Recovery may take several weeks or even months, depending on individual circumstances.
It’s important to follow all of your dentist’s instructions to ensure successful healing and achieve the desired results of bone augmentation. Additionally, regular check-ups and oral care are crucial for maintaining the long-term success of the augmentation.